Freezer purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What you need to know
- Whether it’s strawberries from the garden, leftover cake from the last birthday, or bread rolls for Sunday brunch, a freezer offers the possibility of preserving food over a long period of time.
- In addition to the typical floor-standing appliances, there are also mini versions for smaller needs, as well as built-in and under-counter versions that fit seamlessly into the kitchen unit.
- Depending on your needs and placement, a different size, freezer class, and noise emission is suitable.
- Modern appliances are equipped with anti-frost technologies, among other things, making the cumbersome defrosting unnecessary.
- Unlike chest freezers and fridge-freezers, upright freezers offer more organization options thanks to their various compartments and drawers.
Not just a coolbox — a cool box
Be it a bountiful garden harvest, leftovers after a big party, or frozen store-bought meals for the week, a freezer allows you to easily store food over long periods of time. By contrast to, say, a small built-in freezer compartment of a refrigerator, freezers provide you with more space. That way, you can store more than just a couple of frozen pizzas and few ice cubes. With separate drawers and compartments, you can store frozen meals in, say, Tupperware and still have space for a big bag of ice cubes as well as an ice cream drawer.
The shelf life of goods
At a maximum temperature of -0.4 °F (-18 °C), fruit and vegetables can be stored for 12 to 24 months, depending on the variety. Cooked meat, on the other hand, will only last 3 to 6 months, raw meat up to 12 months, and fish about 4 months.
Large families with big storage needs or commuters with a hectic workday get their money’s worth with a freezer. Instead of cooking fresh every day, you can cook many portions at once and store them in the freezer to take with you for lunch or have something home-cooked to just heat up in the microwave when you get home — also known as meal prep. Aside from preventing food from going bad for longer than fridges, freezers also preserve its nutritional value. After all, fridges operate at above freezing temperatures, whereas freezing goods preserves their vitamin and mineral content. The price of a freezer depends primarily on your requirements. Although affordable freezers are available for as little as $100, they are comparatively small with a volume of 2,8 cubic feet at most and lack innovative features like a no-frost or quick-freeze function. Somewhat more space (2,8 to 7,1 cu ft) is available in appliances in the mid-range between $200 and $500. If you don’t want to miss out on any convenient functions, you will have to spend up to $1500 on premium appliances. In addition, some manufacturers offer luxury models with prices as high as $8000. Such premium appliances contain numerous extras such as an ice cube maker or LED lighting.
Freezing through the ages
Although we may nowadays take the ability to freeze goods for granted, the road to developing freezing technology has been long and arduous:

How a freezer works
A modern freezer is ultimately nothing more than a refrigerator with even lower temperatures, all the way down to -0.4 °F (-18 °C). In terms of their construction, all models are similar: While the insulated outer shell prevents heat from entering the interior, the thermostat and compressor ensure that the desired temperatures are reached. To do this, freezers use a special liquid that cools down when it evaporates. The chemical evaporation effect and thus the cooling cycle of a freezer works as follows:
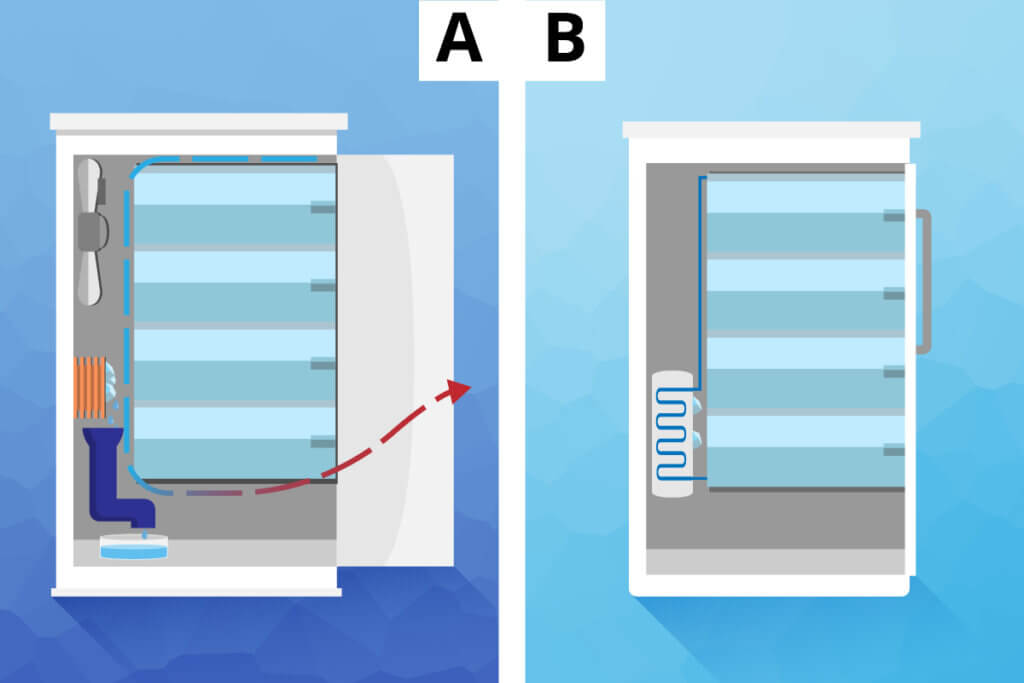
- The liquid refrigerant absorbs heat in the evaporator and evaporates.
- The compressor directs the now gaseous refrigerant into the condenser, where it is subjected to increased pressure.
- The pressure causes the heat to be released to the outside into the ambient air and the refrigerant becomes liquid again.
- The refrigerant returns to the evaporator via the throttle valve, where heat is absorbed, and the pressure is reduced.
- The cycle then starts again from the beginning until the set temperature is reached.
Since the selected temperature refers to the upper temperature limit, the compartments stored below may be even colder. The temperature difference within the freezer occurs due to the fact that heat rises and cold sinks. Therefore, when sorting your frozen goods, make sure to keep in mind that food that is to be preserved for longer should be stored in the bottom.
Popular freezer alternatives: chest and fridge freezer at a glance
Chest freezers or fridge freezers are the main alternatives to the classic freezer. But for whom are these freezers suitable and when is it better to have a separate freezer?

Chest freezers
Regular stand-alone freezers tend to be slim and tall, whereas chest freezers are short and wide. Due to the larger ground surface, they take up more space, and are a better fit for larger rooms such as basements, where they are not in the way. The biggest drawback of a chest freezer is its lack of compartments and drawers. In addition, chest freezers rarely have practical extra functions. If you don’t have much space or care about having an organized freezer, a chest freezer likely isn’t the right fit.
Fridge freezers
If you don’t have much space available, you should opt for a fridge freezer — a combination between a fridge and a freezer. Similar to freezers, these appliances are slim and tall. Unlike refrigerators with a freezer compartment, the freezer section is a separate unit with an independent cooling circuit and its own door. The freezer section usually takes up about a third of the total volume. Due to their limited capacity, hybrid solutions of this kind are particularly suitable for those who only have little to moderate need of frozen goods.
The freezer types: classic, built-in, or mini?
Like refrigerators, freezers come in various types. There are classic freestanding models, built-in freezers, as well as mini appliances. Which freezer is most suitable, depends on your needs and preferences.
Upright freezers: the spacious classics
Upright freezers are available in different sizes. As a rule, the width of such freezers varies between 24 and 28 inches and the height between 47 and 77 inches. With an average capacity of between 5,3 and 12,0 cubic feet, which exceeds the capacity of a conventional fridge-freezer many times over, they take up a lot of space in a kitchen. That is why they are often stored in cellars or storage rooms. Due to their size, upright freezers are particularly suitable for multi-person households and large families.
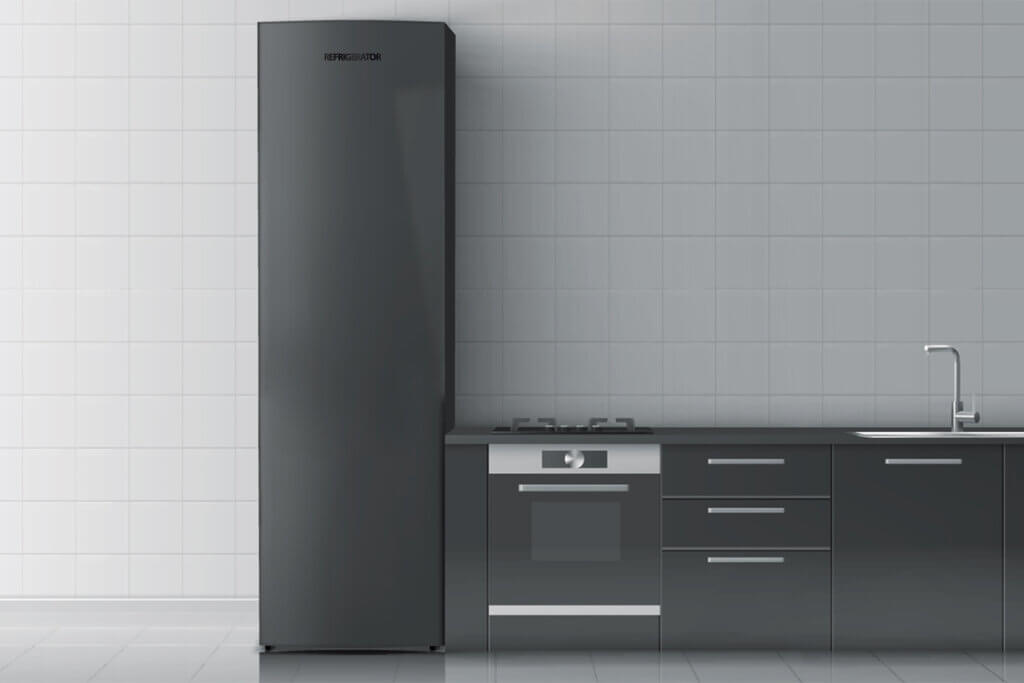

Most upright freezers weigh 135 to 175 pounds empty. Unlike built-in or under-counter units, they are not fitted under worktops or behind kitchen fronts but can be freely positioned anywhere where there is enough space.
In terms of design, buyers can also choose from several options — from classic white to modern stainless steel. Depending on the model, the appliance has a single door or double doors that make the upright freezer a real eye-catcher in the kitchen. The interior is usually divided into several compartments and drawers that offer different amounts of space, so that nothing stands in the way of neatly sorting your food.
Advantages
- Large freezer compartment
- Flexible positioning
- Different sizes and designs
- Easy organization due to compartments and drawers
- Slim versions available
Disadvantages
- Additional parking space required
- Comparatively expensive
Built-in and under-counter freezers: a seamless fit
Under-counter freezers are appliances with standardized dimensions for the kitchen. Since they do not have a cover plate, they can simply be set up under the worktop. With a standardized width of 24 inches and a height of between 23 and 32 inches, they fit under any standard kitchen counter.
Built-in models, on the other hand, are covered with a matching front, which allows them to fit seamlessly into any kitchen unit. With a usually standardized width of 21 inches, they are somewhat narrower than under-counter units, but they vary more in height, between 28 and 70 inches. This means that the external dimensions are smaller than those of a floor-standing appliance, which makes them particularly suitable if there is little free floor space available. On the other hand, the capacity is only 1,7 to 3,4 cubic feet and is thus significantly smaller.
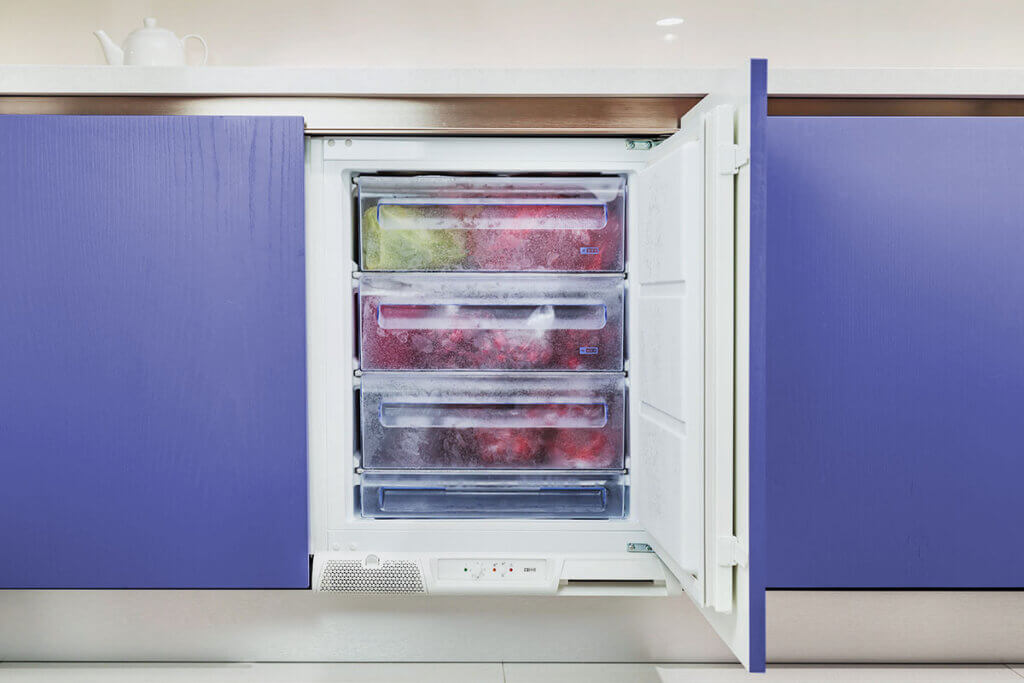

Both versions blend harmoniously into the kitchen. If you place a lot of value on a uniform kitchen front, a built-in freezer is an elegant solution. Under-counter models, on the other hand, are still recognisable as electrical appliances, but offer a space-saving option. Another advantage is the damping of the operating noise by the surrounding furniture front. Due to the adaptation to standard dimensions, however, built-in and under-counter freezers are on average a third more expensive than appliances of the same size without the possibility of integrated installation.
Advantages
- Can be integrated into kitchen unit
- Space-saving
- Uniform front for built-in version
- Insulation of the operating noise
Disadvantages
- Less flexible placement
- Dimensions must fit precisely
- Low useful capacity
- More expensive than units without installation option
Mini freezers: the compact solution
Mini freezers, also known as table-top freezers, usually hold between 1,1 and 1,3 cubic feet and are thus significantly smaller than conventional freezers. The compact models are often no taller or wider than 20 inches. Thanks to their small size, they can be placed in any kitchen, storage room or even on shelves. However, the smaller devices naturally also offer less space. They are primarily designed for smaller spaces, such as offices or student dormitories. In addition, there are special models for caravans and motorhomes that run on the car battery connection or on bottled gas.

Usually, the mini freezer is divided into at least two sections. Since the compact appliance offers little space, if the frozen food is used up quickly, you can switch it off until the next shopping trip to save electricity if necessary. An additional advantage is that mini freezers are very quiet.
Advantages
- Compact and space-saving
- High mobility thanks to the low weight
- Can be easily switched off when not in use
- Quiet in operation
Disadvantages
- Low capacity
- Mostly only two compartments
The most important purchase criteria
The main criteria when choosing a freezer include size, extra features, and price. Since the freezer is in operation around the clock, users should also consider the operation noise and the energy efficiency class. In the following, we will explain what to look out for when buying a freezer.
Capacity
Depending on the needs or the size of your household, a different capacity is suitable. The most relevant factor is the net capacity, i.e. the usable capacity. This is the actual available freezer space, minus accessories, shelves, containers, and the housing. A rule of thumb is to calculate about 1,3 to 2,6 cubic feet per person. However, this also depends on the storage behavior of the respective person: Users who frequently freeze larger quantities of food are better off with a capacity of 3,5 to 4,6 cubic feet. In addition, certain professionals or hobbyists, such as anglers, hunters, or fruit and vegetable gardeners, might need more freezing space than the average consumer. If, on the other hand, you only want to store one or two frozen meals, you will be well served by a smaller appliance.
The freezer always refrigerates the entire net capacity. This means that buying a model that is too large and leaving freezer drawers empty results in unnecessary energy consumption which has a negative impact on both the environment and your bottom line. When choosing the appropriate capacity, the following rules of thumb apply:
Households with one or two people, for example singles or couples, should choose a more compact appliance with a maximum net capacity of 5,3 cubic feet.
Families with three to four people or larger flat-sharing communities usually need a unit with a net capacity of 6,4 to 9,9 cubic feet.
For households with particularly large storage space requirements, freezers with a net capacity of over 12,3 cubic feet are a viable option.
Installation location
The optimal size of the freezer largely depends on the desired location. For one, there should be some distance to the wall — 4 inches are often recommended — so that the compressor does not overheat. Secondly, there should be enough space available to open the appliance door without any hindrance. In addition, the ambient temperature is important: In a cooler room, the freezer requires less energy to reach the necessary temperature. The higher the ambient temperature, the more often the compressor needs to cool, and the more electricity the appliance consumes. A set up near the heater, the oven, or the dishwasher should therefore be avoided.
Energy efficiency
An equally important criterion when buying a freezer is its energy efficiency. In addition to being environmentally friendly, an energy efficient device also saves you money in the long run. Older appliances are often power guzzlers that consume almost twice the energy of today’s standard freezers.
However, the actual power consumption always depends on the individual use and location of the appliance. High-quality freezers have improved energy efficiency due to very good thermal insulation through door seals and modern cooling systems and are therefore particularly energy-saving.
From cool to tropical: the climate classes
The climate class refers to the ambient temperature around the appliance. A freezer with a certain climate class should not be placed in a room that falls outside that range for a prolonged period. There are four classes:
- Subnormal (SN): 50 to 90 °F (10 to 32 °C)
- Normal (N): 61 to 90 °F (16 to 32 °C)
- Subtropics (ST): 61 to 100 °F (16 to 38 °C)
- Tropics (T): 61 to 109 °F (16 to 43 °C)
If you want to put the freezer in a cool cellar, for example, you should go for an appliance with climate class SN so that the freezer works efficiently. However, the temperatures must not be too low, as, in this case, the food could defrost and damage the appliance due to the compressor no longer switching on. The higher the ambient temperature, the greater the temperature difference and the more freezing power the appliance has to generate to compensate. Hence, if you want to keep your electricity costs as low as possible, you should choose the appropriate climate class.
Freezing capability
In terms of cooling capability, freezers are divided into four categories, each marked with a star:
| Stars | Minimum temperature | Shelf life |
| * | up to 21 °F (-6 °C) | 1 week |
| ** | 21 to 10.4 °F (-6 to -12 °C) | 2 weeks |
| *** | 10,4 to 0.4 °F (-12 to -18 °C) | 3 months |
| **** | -0.4 °F(-18 °C) and less | 1 year |
Depending on the number of stars, the appliances are suitable for short-, medium-, or long-term food storage. This is because a freezer with more stars has a lower minimum temperature and allows for longer storage times. Nowadays, there are almost exclusively models with at least three stars on the market. The freezer’s minimum temperature can be recognized by the ice crystal symbols.
Noise emission: from a low hum to a loud buzz
One drawback of a freezer is that it emits noise. This is particularly noticeable if you spend a lot of time close by, for example, if the appliance is located near the dinner table. If it is located in a pantry, storage room, or cellar, the operating noise level is less relevant.
If the decibel (dB) values of the freezer are below 35 dB, they will be barely perceptible. Noise above 40 dB is slightly audible. At about 45 dB is where some people might feel disturbed. However, this differs from person to person. The noise level of modern fridges ranges between 35 and 42 dB, which is roughly comparable to the volume of a whisper. Consumers can find the information on the noise emission of the appliance either on the energy label or on the product data sheet.
Freezer features
Every freezer should have certain basic features. Some useful ones include a digital display, various drawers, and an ice cube dispenser.

Display
Most modern freezers are equipped with a display on the outside. This means that users do not have to keep opening the doors to reach the controls. Ideally, it is easy to see and intuitively designed. With a display, for example, the temperature can be set and adjusted as needed to control energy consumption. Users can also use it to activate functions such as shock-freezing.
Flexible sorting
In freezers with a flexible storing option like VarioRoom (Miele), VarioZone (Bosch, Siemens), or VarioSpace (Liebherr), the shelves and drawers are removable so that they can be arranged flexibly. Some have large-capacity drawers, making it easy to store bulky items. Other appliances are also equipped with freezer trays, as well as telescopic and roller systems to make pulling out compartments easier. Depending on the size, the interior has a different number of partitioning options. While smaller appliances have three to four compartments or drawers, larger models have five to seven separate sections. Such a system helps to store the contents neatly so that you do not have to search through every compartment for a particular frozen good.

Ice cube dispenser
A freezer with an ice cube dispenser prepares fresh ice cubes at the touch of a button. This is a particularly useful function for hot summer days, where you want to consume cold drinks to cool off. However, the dispenser increases energy consumption and takes up storage space. A distinction is made between models with and without a water supply. While the former require a water connection and are always supplied with fresh water from the tap, appliances without a water supply need to be filled and cleaned manually on a regular basis. The Siemens iQ500, for example, has the so-called iceTwister, which drops up to 20 ice cubes into the collection container at the touch of a button.
Feet and castors
Many freezers have height-adjustable feet so that the appliances can compensate for an uneven floor and remain stable. If they also have castors, even the heaviest models can be moved without much effort. As a rule, modern appliances are equipped with castors at least on the rear.
Convenient extra functions
Since the convenience of a freezer also depends on its features, many consumers ask themselves which functions are useful and what they can do without. With innovative functions, for example, food can be frozen in a particularly energy-saving way. Although almost all appliances now have standard features including temperature control and door alarm, some additional features, such as a memory function or even dynamic cooling, provide even more functionality.
Say goodbye to defrosting: anti-frost technologies
Defrosting the freezer is a nuisance: on the one hand, the melted ice water runs everywhere, on the other hand, the food has to be stored somewhere else for a short time, and the appliance has to be cleaned. To spare you from frequent defrosting, modern models have technologies to reduce ice formation. This not only has a positive effect on the maintenance effort but also on the power consumption.
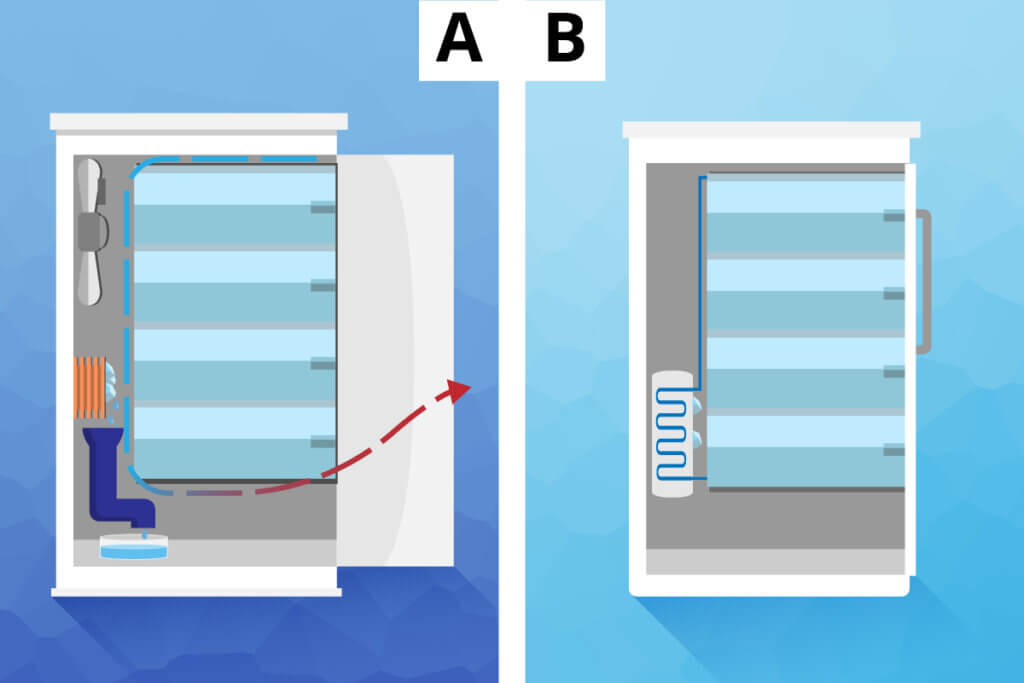
The No Frost technology
The so-called No Frost technology prevents thick layers of ice from forming inside the freezer or in the drawers, which are difficult to defrost. A fan removes moisture from the air and frost settles on the cooling fins. The integrated heater heats the cooling fins at regular intervals, defrosting the thin layers of ice. The resulting defrost water finally reaches a container via the drainage channels and evaporates. In everyday use, such appliances consume more electricity, however, you end up saving energy on the other end, by not having to go through the elaborate defrosting processes. This function keeps the air inside dry. The humidity then condenses, for example, when the appliance door is opened. This technology is usually combined with automatic defrosting, which is used if ice has formed despite the No Frost function.
The Low Frost technology
Unlike the other technologies, Low Frost does not use a fan. However, since the evaporator is located outside the freezer compartment, it does not accumulate frost. The Low Frost system does not completely prevent ice formation, but it keeps it low, so that manual defrosting is only necessary every one to five years.
Gentle fast freezing thanks to shock-freeze function
During slow freezing, large ice crystals form which lead to the destruction of cells and thus to a change in the taste and consistency of the food (also known as freezer burn). Therefore, the freezing process should be as fast as possible. Quick freezing results in the formation of smaller harmless ice crystals that do not destroy nutrients or affect the taste of the food. Basically, the faster fresh food is frozen, the better it is preserved.
The best option is shock-freezing, which is a feature of many modern freezers. Depending on the manufacturer, it might have a slightly different name. Liebherr calls the technology “SuperFrost”, Bauknecht “Shockfreeze”, and Siemens “superFreezing”.

With this particularly gentle function, food is frozen at -22 °F (-30 °C), forming a thin layer of ice around it. The shock-freezing function also prevents the food already stored from thawing when the freezer is opened. Usually, thanks to a sensor, this process switches off automatically after a few hours once the food has frozen through, so you don’t have to worry about anything, in this case.
However, this function is also associated with higher power consumption, as the compressor runs more frequently or for longer. Therefore, it is worthwhile if consumers want to freeze larger quantities on a regular basis. High-performance appliances are designed for shock-freezing more than twelve kilograms of food per day.
Safety features
Every time the freezer door is left open too long or is not closed properly, cold is lost, consuming energy unnecessarily; in the worst case, all frozen food will go bad. To prevent this scenario, many freezers have a built-in alarm function that emits an acoustic signal if the door is left open for too long.
Often, this function is associated with a thermostat that reports an unwanted temperature drop in the freezer. This additional function not only benefits users in the event of a power failure, but also helps them to freeze even more energy efficiently.
Further special features
Apart from the aforementioned features, some modern freezers have other useful ones:
- Memory function: A sensor detects how often the freezer is opened during a certain period of time and saves the data, which allows the freezer to optimally adjust the freezing intensity. For example, if the door is opened often between 7 and 8 p.m., the device will automatically cool the temperature down regularly during this time so that the food does not thaw.
- Dynamic cooling: Dynamic cooling ensures equal temperature zones in the interior of the freezer thanks to regular air circulation, which means that new frozen food cools down faster while the temperature of food already stored does not rise or drop. In the Siemens iQ300, for example, this function is called MultiAirflow.
- Eco function: With the help of this function, the freezer automatically adjusts its freezing intensity to the load. It reduces it when the load is lower, which saves electricity.
Tips for cleaning your freezer
If you want the freezer to last for a long time, you should treat it right! Careful handling begins with the installation of the appliance. A freezer needs enough space to dissipate the heat it produces. For this reason, the ventilation slots must not be covered or place too close to a wall or other furniture.
Since you store food in it, the freezer should be particularly clean. Regular cleaning prevents bacteria and germs from forming and multiplying. For cleaning, it is first necessary to remove all removable parts and then wipe them down with a soft cloth and household cleaner, or water and washing-up liquid; pay particular attention to nooks and crannies, as they are often overlooked. If the dirt is stubborn, a cleaner based on vinegar, citric acid, or chlorine can be used. However, you should first test whether the material tolerates such cleaning agents by applying a small amount to a small area and waiting ten minutes. If the area becomes discolored, the agent is not suitable. Afterwards, take care of the interior as well as the exterior surfaces.
Is it necessary to defrost?
Regular maintenance includes defrosting. This prolongs the shelf life of the appliance and also reduces energy costs. A thick layer of ice can not only damage the goods and take up space, but also hinder the heat-cold exchange, which means that the compressor has to work harder. With most modern appliances, the annoying manual defrosting is no longer necessary, as they are equipped with anti-frost technology.
It is also important to clean the rubber seals and maintain them with glycerine or silicone-based agents. For cleaning the drain hole, it is recommended to use a cotton swab. To eliminate unpleasant odors, you simply wipe out the interior with a water and lemon or lemon and baking soda mixture after cleaning.
Images 1–4: © FinalCheck | Image 5: © sveta / stock.adobe.com | Image 6: © KPad / stock.adobe.com | Image 7: © Gecko Studio / stock.adobe.com | Images 8–13: © FinalCheck












 2,200 reviews
2,200 reviews


